Energy / Resources
-
Is this the fate that awaits Australian Iron Ore Producers?
Roger Montgomery
July 26, 2012
 Could it get any worse for Iron Ore? It Just did!
Could it get any worse for Iron Ore? It Just did!News Flash! Shipping more iron ore volumes at lower prices is the same as JBH and HVN selling more TV’s a lower prices. Margins compress and profits don’t meet expectations.
Back in April, when we began more urgently warning investors to look carefully at profit assumptions for the big material stocks, our theory was that iron ore prices would decline because of a massive supply response. It really was basic supply and demand. Economics 101. You can read our warning here: http://rogermontgomery.com/is-the-bubble-bursting/
Back on December 8 2011, with BHP trading at more than $37.00 we again warned:
“I now wonder whether we are seeing the bubble slip over the precipice? Falling property prices (10 per cent of the Chinese economy) leads to lower construction activity, leads to declining demand for Australian commodities, leads to falling commodity prices, leads to big drops in margins for a sizeable portion of the [Australian stock] market index…”
The doubters and many analysts that cover the sector however told us that lower prices would just mean that BHP, RIO and FMG would simply ship more volume. Remember share price performance over the long run follows profitability not profit.
And here’s the latest…
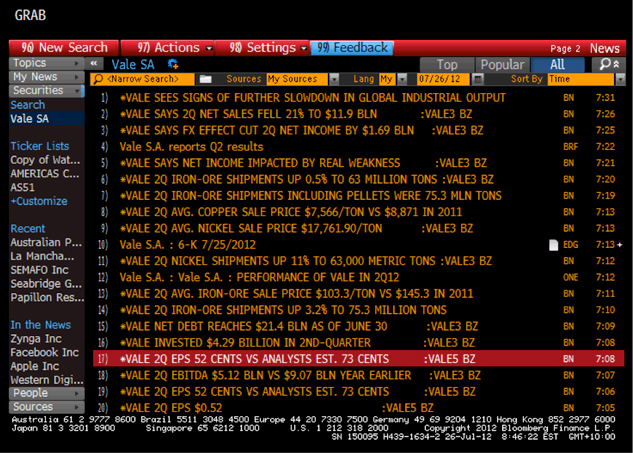
According to a news article that landed in the Bloomberg terminal this morning (see screenshot), Rio de Janeiro-based Vale, the world’s largest iron- ore producer, said second-quarter profit plummeted 59 per cent after prices for iron ore, nickel and copper declined.
Net income dropped to $2.66 billion, or 52 cents per share, from $6.45 billion, or $1.22 per share a year earlier. Vale was expected to post per-share earnings of 73 cents. The selling price of iron ore and most of Vale’s main products is lower than in 2011. This explains the decline in earnings.
Net sales fell 21 percent to $11.9 billion despite an increase in supply / production at Carajas, its biggest mine. Vale reportedly sold its iron ore at an average $103.29 per metric ton, down from $145.30 last year – something we have been warning for 6 months may happen. Nickel’s average sales price dropped 31 percent and copper declined 15 percent.
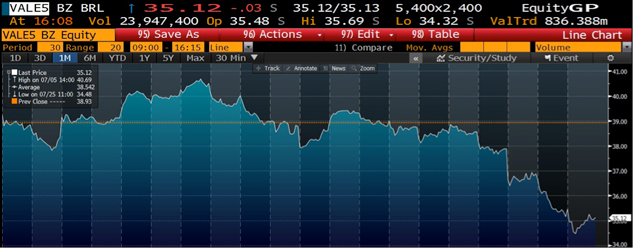
The stock has fallen 24 percent in the past 12 months, twice the 12 percent decrease in Brazil’s benchmark Bovespa Index. Management has put the focus of the fall squarely on slowing economic growth in China, the world’s biggest steel producer.
Returning to BHP, just 12 months ago, analysts had forecast 2012 net profits of almost $22b rising to $23b in 2013.
Those forecasts now stand at $17b and $18b respectively, representing a massive 22%-23% downgrade. And like Vale, BHP has also materially underperformed the ASX 200 index.
And given the significant miss by Vale analysts this morning, we reckon forecast earnings for BHP, RIO, FMG, MIN, AGO, BCI might disappoint again in the near future.
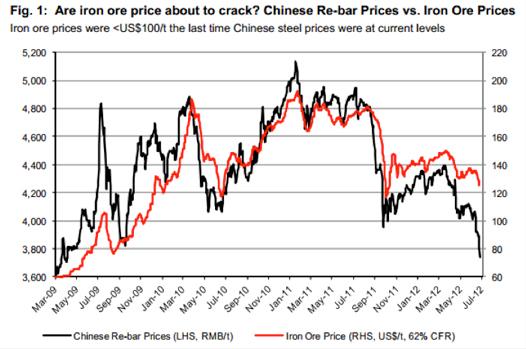
The answer in future periods may in fact lie in the Shanghai Re-bar prices and we have been watching this closely. Why? Because this is the most-traded steel futures contract and last week it hit a 2012 low.
Are iron ore prices, currently trading around China’s cost of production of $120/t, about to follow Re-bar prices despite most predicting the price simply cannot fall past this point?
The last time Re-bar prices were at this level, iron ore prices were also significantly lower.
When I was last on the ABC’s Inside Business program (watch it here: http://rogermontgomery.com/an-important-announcement/), we discussed Fortescue Metals CFO stating that their long-term iron ore price target is $100/t. I wonder how long we will have to wait until that forecast is also revised lower? As always, time will tell. Vale’s news is not a good omen.
by Roger Montgomery Posted in Energy / Resources, Market Valuation.
- save this article
- POSTED IN Energy / Resources, Market Valuation
-
Is this more evidence of downward pressure on commodity prices?
Roger Montgomery
July 24, 2012
 As we have been actively commenting since the start of the year, a key thematic concern we hold for investors in both Mining and Mining services businesses was the potential for commodity prices and in particular Iron Prices to begin to fall. In such an environment, falling prices would result in lower profits and cash flows for our miners and hence we could see significant future risk of projects being either scaled back or shelved in future periods.
As we have been actively commenting since the start of the year, a key thematic concern we hold for investors in both Mining and Mining services businesses was the potential for commodity prices and in particular Iron Prices to begin to fall. In such an environment, falling prices would result in lower profits and cash flows for our miners and hence we could see significant future risk of projects being either scaled back or shelved in future periods.Our view is anchored by a supply response in two new Pilbara regions coming on stream over the next few years and also falling demand from the world’s biggest consumer of additional supply, Asia (China).
With Iron Ore falling to $123.6/t, down 9% in two weeks; we are now at a critical juncture.
Critical because this is the price considered by many to be the ‘floor’ / the most Iron Ore prices can fall given China’s own estimated cost of production is $120/t. This compares to Australia/Brazil at $40/t and Canada/USA/Europe $65/t. A price lower than $120/t would make China’s Iron Ore production uneconomic and hence, a fall below this level “just cannot occur”.
Our experience with commodity producers is a little different. Our experience tells us that marginal producers are the first to lose when commodity prices fall materially.
And in this light we continue to expect over the coming months and years we will see lower prices and perhaps, marginal / high cost producers suffering and mining services starved of work. Even if they are operating at full steam right now.
To ask a question: is the recent moratorium of all Greenfield exploration activities by BHP a sign that they see the world in a similar light?
by Roger Montgomery Posted in Companies, Energy / Resources, Investing Education.
-
The Weekly Kick Off: Is Australia THAT expensive?
Roger Montgomery
July 23, 2012
My Thoughts from the weekend:
A year ago we felt like Churchill – a voice in the wilderness – when we said Iron Ore prices could get ugly. On Friday they did….again. But more on that another time.
The number of overseas visitors we are meeting that tell us Sydney and Australia are “expensive” has got me thinking that Australians and Australia really needs to take advantage of the high Aussie dollar while it lasts.
Feeding ten people in Thailand at a local restaurant and ordering entree, mains and dessert for everyone as well as cocktails, beers, wine and mocktails for the kids amounts to 2000 baht or A$65.00. Thats a main course, a glass of water and a side of fries in Sydney. Its not surprising then to see so many Chinese, Russian and British tourists taking advantage of Thai hospitality.
Thinking about British investors; some have, over their lifetime, amassed, a million pounds. You would think that anyone in this position would be thinking “I’ve made it!” But they can now look forward to retirement with their next egg earning…wait for it… £7,500 per year! No wonder the UK student one of my colleagues is billeting here in Sydney has complained about how expensive Sydney is. The same might be said by Japanese tourists who are likewise earning less than 1% interest on their lifetime savings.
And last week I entertained two Singaporean investment professionals that couldn’t believe how expensive our harbour city had become for them. Coming from Singaporeans and Londoners, that’s really saying something.
These examples may only be anecdotes but my experience as an unconventional investor has taught me that aggregated anecdotes equals the whole.
Australia is uncompetitive.
I just bought a pair of italian shoes online and initially baulked before handing over my credit card details because the price was presented in Euros. But after doing the conversion I realised the depression in Spain (and it IS a depression) had opened another door for Australian shoppers looking for bargains (they have long enjoyed the bargains offered by the US). Additionally another nail has been driven into the coffins of Australia’s department stores.
It’s not often I can clearly see the headline many years in advance but unless our Australian dollar falls back to US70 cents the headlines will read: DJ’s and MYER are now in Run Off!!!!! Even a merger of the two wouldn’t help.
But hope for Australian retailers may be on the horizon. In the last week a consulting exploration geologist and an asset management consultant – both consulting to BHP, RIO, and others – have told me that projects are being shelved and deferred at a rapid pace. In some cases only from Q3 and Q4 to 2013 initially. In other cases, where the miners were shouting only six months ago (when we were writing our bearish opinions on Iron Ore and China); “get as many drills and people as you can, just get it done”, they are now saying “we may look at it again in a couple of years.”
Meantime American banks have been aggressive in cleaning up their banking system. The Economist notes that “the five biggest banks wrote off more almost $500 billion in the aftermath of the financial crisis and raised $318 billion in fresh capital.” No eurozone bank has yet set aside more than $30 billion.
In short I don’t believe a high Aussie dollar can be sustained – at least against the US (unless Agriculture can meet the slack from lower materials prices). And lest you want to be a tourist that complains of high prices when travelling abroad in the future, you need to think about how the above influences will impact your buying power.
The other thing that has caught my attention is the massive growth that will occur in superannuation. Currently there is $1.3 trillion and assuming certain growth rates, expect it to hit $4 trillion in fifteen years. The demographics will ensure that from 2028 (perhaps a couple of years later because of the change from 9% to 12% contributions) we will start seeing outflows putting pressure on inflows. But in the meantime the impact of this? Not enough high quality listed companies, prices of high quality listed companies being the only ones to sustain high price earnings multiples and lots of business for underwriters and Equity Capital Markets execs as a flood of baby boomers float their businesses to meet the tidal wave of superannuation money. Oh and expect a lot more investment into offshore stock markets and international fund managers like Magellan.
That latter point could be another reason to take advantage of a strong Aussie dollar now.
by Roger Montgomery Posted in Energy / Resources, Financial Services.
-
What business plan?
Roger Montgomery
July 13, 2012
Major mineral sands producer, Iluka Resources, announced this week its 2012-2014 Key Physical and Financial Parameters Guidance” released in February 2012 was “now redundant and as such no longer applicable”.
Discussions with both zircon and high grade titanium ore customers about ordering volumes for the December 2012 half-year have indicated “lower ordering patterns or an unwillingness to commit to volumes except on an “as needed” basis”.
Deteriorating economic conditions, subdued customer confidence in China, continuing weakness in the main ceramic export markets for Spain and Italy and some softening in the US manufacturing sector were all to blame.
We assume these same factors would be affecting most materials exporters. Remain cautious.
by Roger Montgomery Posted in Energy / Resources, Investing Education.
-
Are Chinese construction lay-offs a bad omen for Iron Ore prices?
Roger Montgomery
July 9, 2012
Sani Group, China’s biggest maker of construction machines has announced a cut to its workforce.
Given lay-offs did not occur in the down cycles of 2005 and 2008, this is a clear sign some pain is being experienced in China’s industrial heartland.
Sany’s 60,000 staff produces concrete machinery, excavators, cranes, pile drivers and road machinery. Its revenue exceeds RMB80 billion or US$12.5 billion.
With the tripling in demand for machinery in China since 2001, it appears Sany has recently been selling machines on generous credit terms. As a result the machinery maker saw its net receivables double over 2011.
The slowdown in Chinese construction activity is not a good omen for the iron-ore price, currently US$135/tonne. China’s demand accounts for 63% of iron-ore’s global seaborne trade.
by Roger Montgomery Posted in Energy / Resources, Insightful Insights.
-
..and so it goes
Roger Montgomery
June 5, 2012
 As you already know, despite the enthusiasm for mining service companies back in April, we sold our holdings substantially and in some cases completely. We have not shared our peers’ – some of whom include themselves in the ‘value investing’ camp – enthusiasm for BHP. Our reasoning for this is our thesis regarding iron ore prices, which is unchanged from late last year.
As you already know, despite the enthusiasm for mining service companies back in April, we sold our holdings substantially and in some cases completely. We have not shared our peers’ – some of whom include themselves in the ‘value investing’ camp – enthusiasm for BHP. Our reasoning for this is our thesis regarding iron ore prices, which is unchanged from late last year.Back then it was simply the classic investment response to higher prices. Iron Ore prices between 1985 and and 2004 have traded between $11 and $15 and in real terms since the 1920’s prices have traded between $30 and $45. In 2004 the price of iron ore started rallying and hit $187 in 2007.
Putting aside the fact that iron ore experts now ‘guess’ $140 is the new medium term price and $100 the long term price, the rally in price from 2004 to now has produced a huge investment boom and turned millionaires into billionaires as they revalue their reserves (or other bulls value them for them).
It follows that the investment boom will now produce additional supply. The impact of this additional supply cannot be anything but falling prices.
Well, that was our thesis. And then China began slowing down. We wrote about that too
If you have been a regular to the Insights Blog, you will be familiar with some of our recent thoughts on iron ore here:
April 3) http://rogermontgomery.com/mining-services-a-crowded-trade/
April 18) http://rogermontgomery.com/building-heaps-piles-at-bhp/
APril 11) http://rogermontgomery.com/will-china-demand-iron-or/
And you can watch this video I published here on December 8 last year:
Since July last year BHP is down 30% and RIO down 36%. Since April and early May they are down 15% and 20% respectively. Many investors are now thinking they are cheap. But there is the possibility of a classic Value Trap.
Forecast valuations may yet decline further, even if share prices bounce. Here’s our thoughts…
PORTFOLIO POINT: BHP and Rio’s review of capex programs represents a stark turnaround from comments made just two months ago, and it’s a worrying sign for the rest of the sector.
BHP is trading at three-year lows, Fortescue is down 17% from recent highs and Rio is visiting lows last seen in 2008. If you own shares in any of these companies, only Telstra would have saved your portfolio from a shellacking.
The big caps, however, are not the only stocks that have suffered. Over recent years, it is likely that you would have observed my interest in mining services. That interest was a product of the presence of value for money.
This is a sector I know well and have covered numerous times. I have discussed and brought listed businesses – including Decmil Group (DCG), Forge Group (FGE) and Matrix Composites & Engineering (MCE) – and IPOs – GR Engineering (GNG) and Maca (MLD) – to your attention.
This was mostly at a time when there was little market interest, despite their apparent growth profiles, quality aggregated balance sheets and (now with the exception of MCE) management.
Today, however, that story is very different and I find myself erring on the side of caution when it comes to ‘picks and shovels’.
Each week, a stronger case is building that a key growth engine for capex spending by our miners is slowing – that is, commodity prices are falling.
Take one commodity I have discussed recently: iron ore.
In 2010-11, world iron ore production grew 8.1% (or 227mt) to 2.80bt. Assuming similar growth levels in 2011-12, iron ore production will grow to 3.04bt, an increase of about 237mt. (In a classic supply response, BHP production is forecast to grow by 20%, Rio by 30% and FMG by 25%.)
And assuming China consumes 60% of global production again (highly optimistic), its demand would increase by 136.2mt. However, moderating growth means current estimates for China’s iron ore requirements are half this level. With few other countries growing or competing heavily with China, who will pick up that supply overhang in a low-growth environment?
By 2015, two entire Pilbara regions (700mt) in supply terms are estimated to come onto the market. It’s a far stretch to expect China to absorb 420mt (60%) of that.
The impact, I expect, is pressure on iron ore prices.
Many other commodities are looking like they are set to suffer a similar fate. Record prices over a decade have created an investment boom that is climaxing at a time when global demand is losing interest. And you need two to tango. When soaring supply meets softening demand, lower prices follow.
So what are the implications? Put simply, for those who dig stuff out of the ground and export it, margins and cash flow will be squeezed (a situation I have been monitoring closely and alerting readers to for at least six months). It’s why I haven’t bought BHP.
In previous periods, a revenue squeeze has been a precursor to capex plan deferrals or delays lasting years. Barely economical projects are shelved as miners focus instead on financing core (capital-intensive) operations, rather than aggressive growth targets.
Indeed, the 1990s was a very different period for miners, and those who serviced the mining sector barely made it onto investment radars. Companies struggled to cover their cost of capital and total annual capex was less than $20 billion for the entire mining industry.
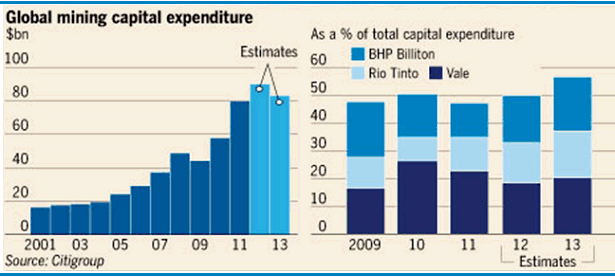
Today, many miners are generating returns on equity in excess of 30% (‘super profits’?) and capex runs in excess of $60 billion per annum. Are such numbers maintainable forever? No. And if it can’t go on forever, it must stop.
Just a few days ago, BHP Billiton and Rio Tinto announced that they are re-evaluating their capital expenditure programs. These comments are in stark contrast to their latest financial reports and presentations made just two months ago.
In those reports, confidence was effervescent and the deployment of $40 billion in a global cash capex spree was on the cards. Today, as China’s growth rate slows and some investors lobby for a greater focus on cost control and returning funds to shareholders, tens of billions of dollars of an extensive development project pipeline is under review.
When the two leading businesses that account for about 35% of total industry investment start to make noise, it’s time to sit up and pay attention.
We are bound to see many other miners follow suit and the chorus is growing louder by the day. Citigroup conducted a survey in April and found that 50% of all miners were considering lowering their investment budgets.
That compares to less than 20% in January.
Figure 1. A picture tells a thousand words
At the start of the financial year, capital expenditure was forecast to rise 34%, with an increase of 18% in 2013.
The forecast today is for a rise of only 13% this year and a fall in 2013. This represents a material deterioration in market conditions in a very short period of time. All of this weighs on the ‘bright prospects’ that once surrounded those companies which service the miners.
This brings us back to Decmil, Forge and investing. I bought both of these businesses in the Montgomery [Private] Fund near its inception.
Forge is a business that has a significant exposure to second-tier miners, especially those expanding their iron ore operations. Decmil, on the other hand, has around 43% of its business exposed to resources and the balance to oil & gas.
While plenty of work is still forecast to be in the pipeline for mining services companies, there are also plenty of companies trying to win it.
If we are at the peak of the current capex cycle, this is as good as it gets in terms of margins for mining services businesses and also workloads.
With that in mind, and coupled with prices increasing to levels I deem attractive for what are businesses with high operating leverage, I have decided to read the writing on the wall and position our investments in a more conservative manner. I sold our Forge holding some weeks ago and also scaled back our holding of Decmil.
It is possible I am early to leave the party – the band is still playing. But the mining industry is bracing for a pullback in investment spending, as the biggest companies reassess their capital expenditure plans amid escalating costs and an uncertain growth outlook. I anticipate that analysts will revise their earnings forecasts lower for 2013 and beyond.
The valuations I look at in Skaffold will also fall, I expect, as those earnings revisions are fed through. Of course, I could also be completely wrong but I reckon the big mining companies’ historical predilections for over-paying for acquisitions (another reason I have been loath to invest) may just revisit them.
The combination of a contracting market and high operating leverage means I simply prefer the safety of cash. Better to be confident of a good return than hopeful of a great one.
This article was first published on May 16, 2012
by Roger Montgomery Posted in Energy / Resources, Insightful Insights, Intrinsic Value.
-

MEDIA
Why is BHP less than a sure-fire thing?
Roger Montgomery
May 26, 2012
In The Australian Roger Montgomery discusses why the laws of supply and demand suggest demanding times ahead for mining companies. Read here.
by Roger Montgomery Posted in Energy / Resources, In the Press, Investing Education.
-

MEDIA
Will increased supply will generate reduced value in commodities?
Roger Montgomery
May 21, 2012
In TheBull.com.au Roger Montgomery discusses his insights into the outlook for Australian commodities share prices over the near future. Read here.
by Roger Montgomery Posted in Companies, Energy / Resources, In the Press.
-
Pumpkins and Mice 2012?
Roger Montgomery
May 16, 2012
 In light of my recent posts about China slowing, the price of iron ore under pressure from a gigantic supply response, our avoidance of BHP/RIO/FMG as investments and our profit taking last month in our mining services holdings…
In light of my recent posts about China slowing, the price of iron ore under pressure from a gigantic supply response, our avoidance of BHP/RIO/FMG as investments and our profit taking last month in our mining services holdings…In April, we warned more frequently than before that the mining boom appeared to be on shaky ground. Of particular interest to us has been the support for Iron Ore prices even in the face of a very great supply response.
If you are keen to study our thoughts on Iron Ore and why we don’t own BHP currently and why we have already sold the bulk of our mining services holdings you can read the following links:
April 3) http://rogermontgomery.com/mining-services-a-crowded-trade/
April 18) http://rogermontgomery.com/building-heaps-piles-at-bhp/
APril 11) http://rogermontgomery.com/will-china-demand-iron-or/
In 2010-11, world iron ore production grew 8.1% or 227mt to 2.8bt. Assuming similar growth levels in 2011-12 – in a classic supply response BHP production is forecast to grow by 20%, RIO by 30%, FMG 25% – iron ore production will grow to 3,037bt, an increase of 237mt.
And assuming China consumes 60% of global production again (highly optimistic), their demand would increase by 136.2mt. However moderating growth means current estimates for China’s iron ore requirements are half this level. With few other countries growing or competing heavily with China, who will pick up that supply overhang in a low growth environment?
By 2015 we estimate that two entire Pilbara regions (700mt) in supply terms will come onto the market. It’s a far stretch to expect China to absorb 420mt (60%) of that. The impact we expect is pressure on iron ore prices.
And finally, just days after BHP and RIO said they are reassessing their development plans…This just flashed across our screens:
*DJ BHP Chairman: World Faces Increasing Volatility, Uncertainty
(MORE TO FOLLOW) Dow Jones Newswires
May 15, 2012 23:37 ET (03:37 GMT)
*DJ BHP’s Jacques Nasser: Australia One Of Higher-Cost Countries For Miners(MORE TO FOLLOW) Dow Jones Newswires
May 15, 2012 23:38 ET (03:38 GMT)
*DJ BHP Chairman: Shareholders Have Lost Confidence In Health Of World Economy(MORE TO FOLLOW) Dow Jones Newswires
May 15, 2012 23:39 ET (03:39 GMT)
*DJ BHP Chairman: Tailwind Of Higher Commodity Prices Moderating(MORE TO FOLLOW) Dow Jones Newswires
May 15, 2012 23:40 ET (03:40 GMT)
*DJ BHP Chairman: Will Redirect Capital If Any Product, Geography Doesn’t Suit(MORE TO FOLLOW) Dow Jones Newswires
May 15, 2012 23:44 ET (03:44 GMT)
DJ BHP Chairman Says Commodity Price Tailwind To Ease FurtherSYDNEY (Dow Jones)–The tailwind of high commodity prices, which have helped the mining
sector report record growth in recent years, is moderating and is expected to ease
further, the chairman of BHP Billiton Ltd. (BHP) said Wednesday.
The sector also faces continuing global volatility and uncertainty since the global
financial crisis, which has led shareholders to lose confidence and focus more on cash
returns and dividend yields, Jacques Nasser said at a business lunch in Sydney.
“Rather than the world settling down, we will face increasing volatility and
uncertainty,” he said. “It is really going to feel as if the ground is shifting
under our feet.”
Nasser described the 2008 crisis as a structural shift and said ongoing developments in
the eurozone were a short time ago “almost unthinkable.”-By Rhiannon Hoyle, Dow Jones Newswires; 61-2-8272-4625
(END) Dow Jones Newswires
May 15, 2012 23:49 ET (03:49 GMT)
Copyright (c) 2012 Dow Jones & Company, Inc.Posted by Roger Montgomery, Value.ableauthor, SkaffoldChairman and Fund Manager, 16 May 2012.
by Roger Montgomery Posted in Energy / Resources.
- 3 Comments
- save this article
- POSTED IN Energy / Resources
-

MEDIA
Why will more production equal less value for Mining Services investors?
Roger Montgomery
May 16, 2012
BHP Billiton (BHP), Rio Tinto (RIO) and Fortescue Metals (FMG) have all announced significantly increased production in the future – on Radio 2GB Roger Montgomery discusses with Ross Greenwood why this, combined with Chinese demand levels is likely to have an adverse effect on their respective share value for some time to come. Listen here.
This program was broadcast 16 May 2012.
by Roger Montgomery Posted in Companies, Energy / Resources, Radio.
- save this article
- POSTED IN Companies, Energy / Resources, Radio