Property
-

MEDIA
Why is the Value of a Property not necessarily what someone is prepared to pay?
Roger Montgomery
April 1, 2012
In the April 2012 issue of BrokerNews.com.au‘s EMag, Greg Campbell of ARAP discusses property valuation issues, and how Roger Montgomery’s Value.able approach to assessing asset values highlights that what someone is prepared to pay can bear very little relation to the true worth of an asset. Read here.
by Roger Montgomery Posted in In the Press, Investing Education, Property.
- save this article
- POSTED IN In the Press, Investing Education, Property
-
Is the bubble bursting?
Roger Montgomery
December 8, 2011
 In 2010 here at the Insights Blog I wrote:
In 2010 here at the Insights Blog I wrote:“a bubble guaranteed to burst is debt fuelled asset inflation; buyers debt fund most or all of the purchase price of an asset whose cash flows are unable to support the interest and debt obligations. Equity speculation alone is different to a bubble that an investor can short sell with high confidence of making money.
The bubbles to short are those where monthly repayments have to be made. While this is NOT the case in the acquisitions and sales being made in the coal space right now, it IS the case in the macroeconomic environment that is the justification for the purchases in the coal space.
China.
If you are not already aware, China runs its economy a little differently to us. They set themselves a GDP target – say 8% or 9%, and then they determine to reach it and as proved last week, exceed it. They do it with a range of incentives and central or command planning of infrastructure spending.
Fixed asset investment (infrastructure) amounts to more than 55% of GDP in China and is projected to hit 60%. Compare this to the spending in developed economies, which typically amounts to circa 15%. The money is going into roads, shopping malls and even entire towns. Check out the city of Ordos in Mongolia – an entire town or suburb has been constructed, fully complete down to the last detail. But it’s empty. Not a single person lives there. And this is not an isolated example. Skyscrapers and shopping malls lie idle and roads have been built for journeys that nobody takes.
The ‘world’s economic growth engine’ has been putting our resources into projects for which a rational economic argument cannot be made.
Historically, one is able to observe two phases of growth in a country’s development. The first phase is the early growth and command economies such as China have been very good at this – arguably better than western economies, simply because they are able to marshal resources perhaps using techniques that democracies are loath to employ. China’s employment of capital, its education and migration policies reflect this early phase growth. This early phase of growth is characterised by expansion of inputs. The next stage however only occurs when people start to work smarter and innovate, becoming more productive. Think Germany or Japan. This is growth fuelled by outputs and China has not yet reached this stage.
China’s economic growth is thus based on the expansion of inputs rather than the growth of outputs, and as Paul Krugman wrote in his 1994 essay ‘The Myth of Asia’s Miracle’, such growth is subject to diminishing returns.
So how sustainable is it? The short answer; it is not.
Overlay the input-driven economic growth of China with a debt-fuelled property mania, and you have sown the seeds of a correction in the resource stocks of the West that the earnings per share projections of resource analysts simply cannot factor in.
In the last year and a half, property speculation has reached epic proportions in China and much like Australia in the early part of this decade, the most popular shows on TV are related to property investing and speculation. I was told that a program about the hardships the property bubble has provoked was the single most popular, but has been pulled.
Middle and upper middle class people are buying two, three and four apartments at a time. And unlike Australia, these investments are not tenanted. The culture in China is to keep them new. I saw this first hand when I traveled to China a while back. Row upon row of apartment block. Empty. Zero return and purchased on nothing other than the hope that prices will continue to climb.
It was John Kenneth Galbraith who, in his book The Great Crash, wrote that it is when all aspects of asset ownership such as income, future value and enjoyment of its use are thrown out the window and replaced with the base expectation that prices will rise next week and next month, as they did last week and last month, that the final stage of a bubble is reached.
On top of that, there is, as I have written previously, 30 billion square feet of commercial real estate under debt-funded construction, on top of what already exists. To put that into perspective, that’s 23 square feet of office space for every man, woman and child in China. Commercial vacancy rates are already at 20% and there’s another 30 billion square feet to be supplied! Additionally, 2009 has already seen rents fall 26% in Shanghai and 22% in Beijing.
Everywhere you turn, China’s miracle is based on investing in assets that cannot be justified on economic grounds. As James Chanos referred to the situation; ‘zombie towns and zombie buildings’. Backing it all – the six largest banks increased their loan book by 50% in 2009. ‘Zombie banks’.
Conventional wisdom amongst my peers in funds management and the analyst fraternity is that China’s foreign currency reserves are an indication of how rich it is and will smooth over any short term hiccups. This confidence is also fuelled by economic hubris eminating from China as the western world stumbles. But pride does indeed always come before a fall. Conventional wisdom also says that China’s problems and bubbles are limited to real estate, not the wider economy. It seems the flat earth society is alive and well! As I observed in Malaysia in 1996, Japan almost a decade before that, Dubai and Florida more recently, never have the problems been contained to one sector. Drop a pebble in a pond and its ripples eventually impact the entire pond.
The problem is that China’s banking system is subject to growing bad and doubtful debts as returns diminish from investments made at increasing prices in assets that produce no income. These bad debts may overwhelm the foreign currency reserves China now has.”
I now wonder whether we are seeing the bubble slip over the precipice? Falling property prices (10 per cent of the Chinese economy) leads to lower construction activity, leads to declining demand for Australian commodities, leads to falling commodity prices, leads to bigs drops in margins for a sizeable portion of the market index…
Watch this video and decide for yourself.
Posted by Roger Montgomery, Value.able author and Fund Manager, 8 December 2011.
by Roger Montgomery Posted in Energy / Resources, Insightful Insights, Market Valuation, Property, Value.able.
-
Is there any value in Property Trusts?
Roger Montgomery
April 9, 2010
 The other day, Andrew Robertson interviewed me for ABC’s Lateline Business Program about property trusts (you can find the transcript in the Media Room, On TV). I thought you might benefit from an expanded précis.
The other day, Andrew Robertson interviewed me for ABC’s Lateline Business Program about property trusts (you can find the transcript in the Media Room, On TV). I thought you might benefit from an expanded précis.For a very long time, property trusts were described rather derisorily as the investments of widows and orphans – boring, uneventful and staid. Then with the advent of a name change to REITS (Real Estate Investment Trusts), cheap credit and a healthy dose of me-too-ism, property trust managers trotted down the path that took them to near extinction.
Managers of today’s REITS are falling over themselves to once again describe themselves as staid boring old property trusts. But don’t be fooled, while a decade of stable returns and the life savings of so many are gone, many of the managers responsible are not.
With some basic arithmetic, let me explain what has occurred. Company A has $10 of Equity per Share that is returning 7% to 11% year-in and year-out. Somewhere between 2005 and 2006, like a kid at a toy shop screaming “I want one too”, the managers of property trusts started expanding in a debt-fuelled binge to get bigger.
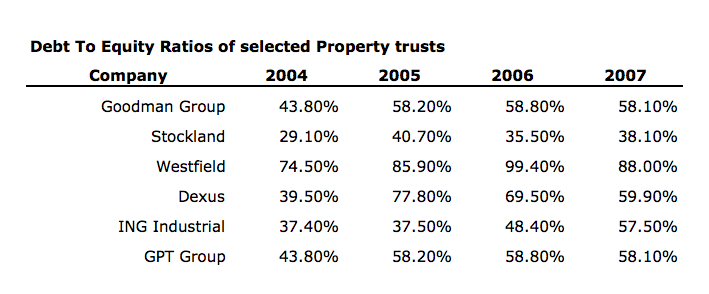
Arguably led by Westfield a year earlier in 2004, and as one might expect, the increased debt produced rising Returns on Equity. But it didn’t last.
The party’s last song may have been August 29, 2007. That’s when Westfield was leading again. It sold a half share of Doncaster Shoppingtown for $738 million to one of the world’s largest property managers, LaSalle, on a yield of 4.7% – a record low. Westfield also sold half of its Westfield Parramatta centre for $717 million at a time when Centro, for example, was still loading up on debt. It sold another $1.3 billion in property-linked notes, launched a UK wholesale fund into which it sold $1.3 billion of its inventory, and sold more than A$750 million of US assets. And while it was selling assets, it was raising $3 billion of capital through a rights issue ostensibly to acquire more assets.
Unfortunately for many investors, the managers of other property concerns thought they were smarter than the Lowys. Have a look at the debt to equity ratios in 2007 and compare them to the corresponding ratios in 2004. And the US was reported to be heading into recession.
While it would be some time before the revelers turned into pumpkins and mice, the band had packed up and gone home.
If you want to set your kids on the road to financial success, tell them this: “If you can’t afford to buy it with cash, you don’t deserve to have it.” Its harsh, but I grew up on that advice. There were a few lay-buys for Christmas, but there wasn’t a single card in my Mother’s glomesh purse.
The lesson however was lost on the property trust managers, and it wasn’t their money anyway!
Eventually everything did turn to pumpkins and mice, and what happened next saved the entities and protected many of the executive jobs but arguably did far fewer favours for the unit holders.
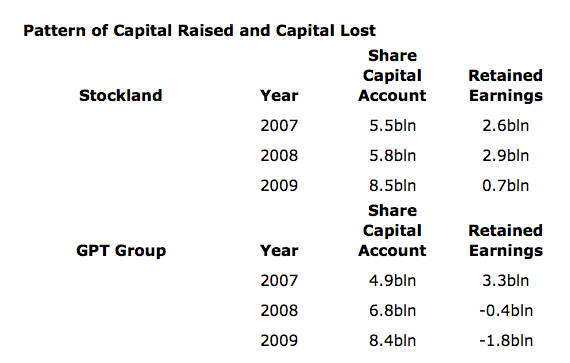
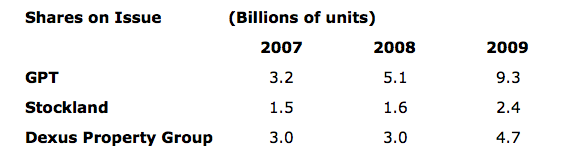
In 2008 Company A writes down its properties, triggering loan covenants and LVR limits. Debt to equity ratio explodes. Bank tells Company A to sort it out. Company A’s share price falls to meaningless price and far below even the written down NTA. Company A conducts a capital raising anyway and issues hundreds of millions of new shares at a discount to the price and in complete annihilation of the equity per share, as the following tables demonstrate.
The result of all this activity, quite apart from the corporate finance fees it generated, was a dilution of Equity per unit, Earnings per unit and Return on Equity.
GPT’s, ING’s and Goodman’s Returns on Equity are expected to average 5 per cent or less for the next two years – that’s less than a bank account. Stockland and Dexus are expected to average 7 or 8 per cent – a little better, but nothing to write home about.
And finally, you can’t dilute Equity per Share, Earnings per Share and Returns on Equity without a reduction in the intrinsic values of these entities, and that’s precisely what has happened.
Stockland’s intrinsic value has fallen from $4.00 in 2008 to $2.16 today. Westfield from $8.25 to $6.71, Dexus from $2.74 in 2007 to 15 cents today and GPT, from $4.10 in 2007 to 30 cents today. Those intrinsic values aren’t going anywhere in a hurry either, unless Returns on Equity can rise significantly, but with debt now substantially lower that appears less likely.
Posted by Roger Montgomery, 9 April 2010.
by Roger Montgomery Posted in Companies, Property.
- 20 Comments
- save this article
- POSTED IN Companies, Property
-
The Lowe’s are the best in the business, but would I buy Westfield?
Roger Montgomery
January 30, 2010
Since early December Paul, Squigly, Steven and Darren have requested I value Westfield. WDC is also a popular stock with viewers of Nina May’s Your Money Your Call on the Sky Business Channel (you can watch highlights at my YouTube channel, just type ‘Westfield’ into the search feature), and rightly so. It’s a company run by three of the most capable men in the world and one whose shares I have owned in the past.
Today its price, according to a number of analysts and strategists, does not appear to have responded to expectations for an improvement in economic conditions in the US. The biggest gap between inventories and orders since the mid 70’s, the decline in housing inventory, the strong turnaround in cyclical indicators and the steep yield curve all suggest an acceleration in US economic growth – by the way if this doesn’t sound like me, you are right. I am just repeating what I have been reading.
I don’t subscribe to the view that it’s the job of the investor to allow macro economic forecasts to influence micro-based investment decisions.
If however the economists are right, and the US economic recovery does gain traction, then all that remains is a recovery in consumer confidence to see Westfield benefit. Of course if the US economic strength is sustained, then one suspects the US dollar will also recover, making Westfield’s profits more valuable in Australian dollar terms.
Those things aside, lets have a quick look at the valuation and take a dispassionate view about the price irrespective of whether others believe the price has or hasn’t responded to US growth expectations. continue…
by Roger Montgomery Posted in Companies, Consumer discretionary, Property.